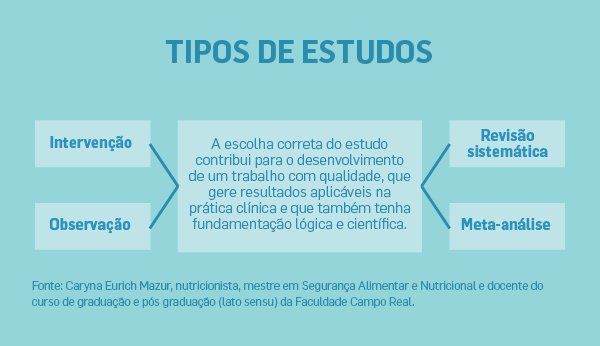
A Nutrição é uma ciência que constantemente é alvo de curiosidade e, dessa maneira, denota grande número de publicações científicas. É fundamental, a partir dos objetivos da pesquisa, a escolha correta do tipo de estudo para que ocorra o desenvolvimento do trabalho com qualidade. Além disso, devem gerar resultados aplicáveis na prática clínica e que também tenham fundamentação lógica e científica, completa Caryna Eurich Mazur, nutricionista, mestre em Segurança Alimentar e Nutricional e docente do curso de graduação e pós-graduação da Faculdade Campo Real. De acordo com ela, os principais estudos na área de nutrição são:
Intervenção: é um estudo no qual o pesquisador propõe intervir na vida do sujeito de pesquisa em algum aspecto. Por exemplo, propor que o indivíduo suplemente 2g de ômega 3 ao dia e ao final de quatro semanas analisar qual foi a melhora/benefício nos resultados bioquímicos e antropométricos. Além disso, estudos de intervenção são muito utilizados em teses de doutorado, quando se objetiva a análise de um produto novo, ou a indicação de um novo tratamento, ou ainda a eficácia da orientação nutricional. São estudos completos, e amplamente aceitos no meio científico, com boa validação e aceitação, avalia Caryna.
Observação: Estudos observacionais são aqueles em que o pesquisador somente observa determinada situação. Por exemplo, o objetivo era verificar o percentual de crianças com sobrepeso e obesidade em creches de uma cidade. Ao final do estudo, foi constatado que mais da metade das crianças possuía esta condição. De acordo com a nutricionista, o estudo observacional pode propor uma intervenção após dada observação e, neste caso, a educação nutricional e orientação seriam pertinentes. São estudos utilizados para obtenção de uma fotografia de certa população. São importantes porque, por meio deles, é possível conduzir demais estudos a fim de aprofundar o tema, analisa.
Revisão sistemática: Diferentemente dos dois primeiros, o pesquisador ao conduzir uma revisão sistemática não tem contato com o sujeito de pesquisa. São estudos aceitos como formadores de opinião no meio científico. A nutricionista afirma que a partir da revisão sistemática é possível estabelecer relações sobre dois fatores, distintos ou não. Por exemplo, a relação entre o consumo de café o risco de desenvolver diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Para este estudo, foram analisados 30 artigos; a partir dos resultados, foi possível concluir que o consumo de café esteve associado com a diminuição da incidência de diabetes. Revisões sistemáticas são recomendadas para conhecimento de relações causais ou não, explica.
Meta-análise: De acordo com Caryna, é parecida com a revisão sistemática, com a diferença que, neste caso, são propostos testes estatísticos para determinar a relação constatada ou não na revisão. Além disso, segundo a profissional, os artigos também têm uma seleção rigorosa e possuem maior validade dentro do meio científico. Por exemplo, meta-análise de como o consumo do chá verde pode auxiliar na diminuição das circunferências corporais. Após aplicada técnicas estatísticas, foi observado que não houve associação (p>0,05) entre o consumo de chá verde (em suas diversas apresentações) e a redução das circunferências, conclui.